Netty启动初始化分析_1
代码示例
MyServer:
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//childHandler的任务由workGroup来执行
//如果是handler,则由bossGroup来执行
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
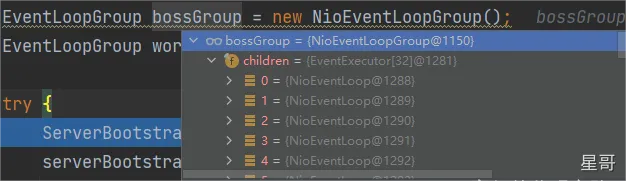
一 创建线程组EventLoopGroup
首先看下执行后的结构
- 默认情况下
bossGroup和workerGroup中的线程个数都为cpu核数的2倍 - 每一个 NioEventLoop 包含如下的属性(比如自己的 Selector、任务队列、执行器等)
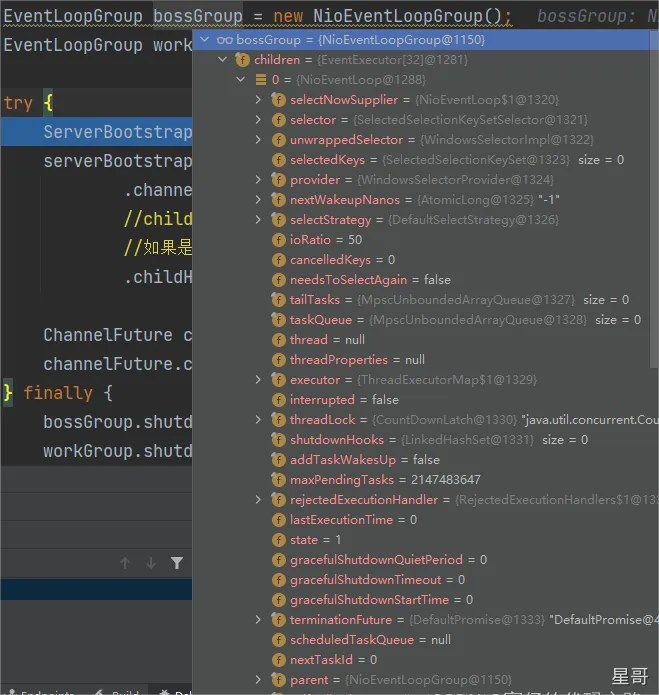
EventLoopGroup
/**
* Special {@link EventExecutorGroup}
* which allows registering {@link Channel}s that get
* processed for later selection during the event loop.
*
*/
public interface EventLoopGroup extends EventExecutorGroup {
/**
* Return the next {@link EventLoop} to use
*/
@Override
EventLoop next();
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop}. The returned {@link ChannelFuture}
* will get notified once the registration was complete.
*/
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel);
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop} using a {@link ChannelFuture}. The passed
* {@link ChannelFuture} will get notified once the registration was complete and also will get returned.
*/
ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise);
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop}. The passed {@link ChannelFuture}
* will get notified once the registration was complete and also will get returned.
*
* @deprecated Use {@link #register(ChannelPromise)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise);
}
EventLoopGroup 是一个线程组,其中的每一个线程都在循环执行着三件事情
select:轮训注册在其中的 Selector 上的 Channel 的 IO 事件processSelectedKeys:在对应的 Channel 上处理 IO 事件runAllTasks:再去以此循环处理任务队列中的其他任务
1调用NioEventLoopGroup的构造方法
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory) {
super(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory, RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject());
}
2调用MultithreadEventLoopGroup的构造方法
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
如果不指定线程数则默认为cpu核数的2倍
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;
static {
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS);
}
}
3调用MultithreadEventExecutorGroup的构造方法
public abstract class MultithreadEventExecutorGroup extends AbstractEventExecutorGroup {
//Reactor线程组中的Reactor集合
private final EventExecutor[] children;
private final Set<EventExecutor> readonlyChildren;
//从Reactor group中选择一个特定的Reactor的选择策略 用于channel注册绑定到一个固定的Reactor上
private final EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser chooser;
/**
* Create a new instance.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads that will be used by this instance.
* @param executor the Executor to use, or {@code null} if the default should be used.
* @param chooserFactory the {@link EventExecutorChooserFactory} to use.
* @param args arguments which will passed to each {@link #newChild(Executor, Object...)} call
*/
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
checkPositive(nThreads, "nThreads");
if (executor == null) {
//用于创建Reactor线程
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
//创建EventExecutor的数组(默认容量cpu核数2倍)
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
//循环创建reaactor group中的Reactor
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
//创建reactor
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
// Let the caller handle the interruption.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// chooser 的作用是为了实现 next()方法,即从 group 中挑选
// 一个 NioEventLoop 来处理连接上 IO 事件的方法
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {
if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
};
for (EventExecutor e: children) {
e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);
}
Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);
Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
}
3.1创建executor
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
3.1.1创建线程工厂
public DefaultThreadFactory(String poolName, boolean daemon, int priority, ThreadGroup threadGroup) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(poolName, "poolName");
if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"priority: " + priority + " (expected: Thread.MIN_PRIORITY <= priority <= Thread.MAX_PRIORITY)");
}
prefix = poolName + '-' + poolId.incrementAndGet() + '-';
this.daemon = daemon;
this.priority = priority;
this.threadGroup = threadGroup;
}
3.1.2创建ThreadPerTaskExecutor
public final class ThreadPerTaskExecutor implements Executor {
private final ThreadFactory threadFactory;
public ThreadPerTaskExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this.threadFactory = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(threadFactory, "threadFactory");
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
threadFactory.newThread(command).start();
}
}
3.2创建EventExecutor newChild(executor, args)
NioEventLoopGroup
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
SelectorProvider selectorProvider = (SelectorProvider) args[0];
SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory = (SelectStrategyFactory) args[1];
RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler = (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2];
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory taskQueueFactory = null;
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory tailTaskQueueFactory = null;
int argsLength = args.length;
if (argsLength > 3) {
taskQueueFactory = (EventLoopTaskQueueFactory) args[3];
}
if (argsLength > 4) {
tailTaskQueueFactory = (EventLoopTaskQueueFactory) args[4];
}
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, selectorProvider,
selectStrategyFactory.newSelectStrategy(),
rejectedExecutionHandler, taskQueueFactory, tailTaskQueueFactory);
}
可以看到返回的就是NioEventLoop
3.2.1 调用NioEventLoop构造方法
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler,
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory taskQueueFactory, EventLoopTaskQueueFactory tailTaskQueueFactory) {
super(parent, executor, false, newTaskQueue(taskQueueFactory), newTaskQueue(tailTaskQueueFactory),
rejectedExecutionHandler);
this.provider = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(selectorProvider, "selectorProvider");
this.selectStrategy = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(strategy, "selectStrategy");
//获得nio的selector
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
this.selector = selectorTuple.selector;
this.unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
}
openSelector()
这里对selector进行了优化
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
//调用jdk底层的api
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
//判断是否需要关闭优化(默认false, 也就是默认需要优化)
if (DISABLE_KEY_SET_OPTIMIZATION) {
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
//通过反射拿到sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl这个类的class对象
Object maybeSelectorImplClass = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
try {
return Class.forName(
"sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl",
false,
PlatformDependent.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (Throwable cause) {
return cause;
}
}
});
//判断拿到的是不是class对象并且是不是Selector的实现类
if (!(maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Class) ||
// ensure the current selector implementation is what we can instrument.
!((Class<?>) maybeSelectorImplClass).isAssignableFrom(unwrappedSelector.getClass())) {
if (maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Throwable) {
Throwable t = (Throwable) maybeSelectorImplClass;
logger.trace("failed to instrument a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector, t);
}
//如果不是他的实现, 直接返回原生select
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
//如果是它的实现, 就拿到其class对象
final Class<?> selectorImplClass = (Class<?>) maybeSelectorImplClass;
//用这个数据结构替换原生的SelectionKeySet
final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet();
Object maybeException = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
try {
//反射拿到selectedKeys和publicSelectedKeys两个属性, 默认这两个属性底层都是hashSet方式实现的
Field selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys");
Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys");
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 9 && PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {
// Let us try to use sun.misc.Unsafe to replace the SelectionKeySet.
// This allows us to also do this in Java9+ without any extra flags.
long selectedKeysFieldOffset = PlatformDependent.objectFieldOffset(selectedKeysField);
long publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset =
PlatformDependent.objectFieldOffset(publicSelectedKeysField);
if (selectedKeysFieldOffset != -1 && publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset != -1) {
PlatformDependent.putObject(
unwrappedSelector, selectedKeysFieldOffset, selectedKeySet);
PlatformDependent.putObject(
unwrappedSelector, publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset, selectedKeySet);
return null;
}
// We could not retrieve the offset, lets try reflection as last-resort.
}
//selectedKeys属性设置成可修改的
Throwable cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(selectedKeysField, true);
if (cause != null) {
return cause;
}
//publicSelectedKeys属性设置成可修改的
cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(publicSelectedKeysField, true);
if (cause != null) {
return cause;
}
//将selector的这两个属性替换成Netty的selectedKeySet
selectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);
publicSelectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);
return null;
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
return e;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
return e;
}
}
});
if (maybeException instanceof Exception) {
selectedKeys = null;
Exception e = (Exception) maybeException;
logger.trace("failed to instrument a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector, e);
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
//将优化后的keySet保存成NioEventLoop的成员变量
selectedKeys = selectedKeySet;
logger.trace("instrumented a special java.util.Set into: {}", unwrappedSelector);
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector,
new SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet));
}
- 使用反射将
selectedKeySet替换了selector对象中的selectedKeys, 和publicSelectedKeys两个属性 selectedKeys = selectedKeySet将优化的数据结构selectedKeySet保存在NioEventLoop的成员变量中,这样, selector在select()操作的过程中, 如果有就绪事件则会将返回的key存放在selectedKeySet所对应的数组中
3.2.1.1 调用SingleThreadEventLoop构造方法
protected SingleThreadEventExecutor(EventExecutorGroup parent, Executor executor,
boolean addTaskWakesUp, Queue<Runnable> taskQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedHandler) {
super(parent);
this.addTaskWakesUp = addTaskWakesUp;
this.maxPendingTasks = DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_EXECUTOR_TASKS;
this.executor = ThreadExecutorMap.apply(executor, this);
//创建任务队列
this.taskQueue = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(taskQueue, "taskQueue");
this.rejectedExecutionHandler = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(rejectedHandler, "rejectedHandler");
}
再进入super(parent);
protected AbstractScheduledEventExecutor(EventExecutorGroup parent) {
super(parent);
}
再进入super(parent);
protected AbstractEventExecutor(EventExecutorGroup parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
NioEventLoopGroup构造方法执行后总结
NioEventLoopGroup构造方法执行完后nThreads数量默认为cpu核数2倍executor为nullchooserFactory=DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.INSTANCEselectorProvider=SelectorProvider.provider()selectStrategyFactory=DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCErejectedExecutionHandler=RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject()
- 父类
MultithreadEventLoopGroup的有参数构造函数创建一个NioEventLoop的容器children = new EventExecutor[nThreads] - 构建每一个
NioEventLoop调用的是children[i] = newChild(executor, args) newChild()方法最终调用了NioEventLoop的构造函数,初始化其中的选择器、任务队列、执行器
二 创建ServerBootstrap
1调用ServerBootstrap构造方法
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
2绑定线程组
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
2.1
ServerBootstrap
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {
super.group(parentGroup);
if (this.childGroup != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("childGroup set already");
}
this.childGroup = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(childGroup, "childGroup");
return this;
}
2.1.1
AbstractBootstrap
/**
* The {@link EventLoopGroup} which is used to handle all the events for the to-be-created
* {@link Channel}
*/
public B group(EventLoopGroup group) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(group, "group");
if (this.group != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("group set already");
}
this.group = group;
return self();
}
private B self() {
return (B) this;
}
执行完serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)可以发现bossGroup赋给了父类AbstractBootstrap,workGroup赋给了ServerBootstrap
3绑定通道
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
3.1
AbstractBootstrap
/**
* The {@link Class} which is used to create {@link Channel} instances from.
* You either use this or {@link #channelFactory(io.netty.channel.ChannelFactory)} if your
* {@link Channel} implementation has no no-args constructor.
*/
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {
return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelClass, "channelClass")
));
}
3.1.1 创建channel实例并赋值给channelFactory
ReflectiveChannelFactory
public ReflectiveChannelFactory(Class<? extends T> clazz) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(clazz, "clazz");
try {
this.constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Class " + StringUtil.simpleClassName(clazz) +
" does not have a public non-arg constructor", e);
}
}
3.1.2创建channelFactory
AbstractBootstrap
/**
* @deprecated Use {@link #channelFactory(io.netty.channel.ChannelFactory)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public B channelFactory(ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelFactory, "channelFactory");
if (this.channelFactory != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("channelFactory set already");
}
this.channelFactory = channelFactory;
return self();
}
4设置childHandler处理器
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new TestServerInitializer());
ServerBootstrap
/**
* Set the {@link ChannelHandler} which is used to serve the request for the {@link Channel}'s.
*/
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {
this.childHandler = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(childHandler, "childHandler");
return this;
}
5绑定端口号
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync();
AbstractBootstrap
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
//初始化和注册
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
5.1 初始化和注册
AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister()
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
// If we are here and the promise is not failed, it's one of the following cases:
// 1) If we attempted registration from the event loop, the registration has been completed at this point.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now because the channel has been registered.
// 2) If we attempted registration from the other thread, the registration request has been successfully
// added to the event loop's task queue for later execution.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now:
// because bind() or connect() will be executed *after* the scheduled registration task is executed
// because register(), bind(), and connect() are all bound to the same thread.
return regFuture;
}
5.1.1 创建channel
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
这时的channelFactory其实是ReflectiveChannelFactory,调用newChannel其实就是在将NioServerSocketChannel实例化
5.1.1.1进入NioServerSocketChannel无参构造
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
/**
* Use the {@link SelectorProvider} to open {@link SocketChannel} and so remove condition in
* {@link SelectorProvider#provider()} which is called by each ServerSocketChannel.open() otherwise.
*
* See <a href="https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2308">#2308</a>.
*/
return provider.openServerSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException(
"Failed to open a server socket.", e);
}
}
可以看到调用newSocket方法后,通过SelectorProvider得到了nio中的ServerSocketChannel
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
5.1.1.1.1调用super进入AbstractNioChannel的构造方法
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
5.1.1.1.1.1再调用super进入AbstractChannel的构造方法
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
5.1.1.1.2调用NioServerSocketChannelConfig的构造方法
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
点击super,直到进入AbstractChannel的构造方法
/**
* Creates a new instance.
*
* @param parent
* the parent of this channel. {@code null} if there's no parent.
*/
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
可以看到ChannelPipeline是在这里进行创建的。
进入newChannelPipeline()方法
protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) {
this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel");
succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null);
voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true);
tail = new TailContext(this);
head = new HeadContext(this);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
可以看到创建了head和tail两个节点,并且首尾相连。
进入DefaultServerSocketChannelConfig的构造方法
public DefaultServerSocketChannelConfig(ServerSocketChannel channel, ServerSocket javaSocket) {
super(channel, new ServerChannelRecvByteBufAllocator());
this.javaSocket = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(javaSocket, "javaSocket");
}
ServerChannelRecvByteBufAllocator为动态的ByteBuf分配器,是根据前一次分配缓冲区的大小来决定下一次分配的大小。
5.1.2 初始化init(channel)
init(channel);
ServerBootstrap#init(Channel channel)
void init(Channel channel) {
setChannelOptions(channel, newOptionsArray(), logger);
setAttributes(channel, newAttributesArray());
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
//childGroup就是workGroup
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
//childHandler就是我们自己定义的ChannelHandler
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions = newOptionsArray(childOptions);
final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs = newAttributesArray(childAttrs);
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) {
// 获取 NioServerSocketChannel 实例的 pipeline
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
//如果之前在serverBootstrap调用了handler方法,
//在这里就会进行添加
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 异步执行向 pipeline 添加 ServerBootstrapAcceptor
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//配置处理器配置的适配器
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
}
5.1.2.1 设置channelOption属性
channelOption主要用来配置channel的网络属性
static void setChannelOptions(
Channel channel, Map.Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] options, InternalLogger logger) {
for (Map.Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: options) {
setChannelOption(channel, e.getKey(), e.getValue(), logger);
}
}
5.1.2.2 netty创建一个ChannelInitializer添加到ChannelPipeline中。
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
//如果之前在serverBootstrap调用了handler方法,
//在这里就会进行添加
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 异步执行向 pipeline 添加 ServerBootstrapAcceptor
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//配置处理器配置的适配器
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
可以看到在初始化init方法内,ChannelPipeline并且自己会创建一个ChannelInitializer添加到ChannelPipeline中。而 ChannelInitializer中的initChannel方法执行时机后续会进行分析。
ChannelInitializer其实是一个特殊的ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
/**
* A special {@link ChannelInboundHandler} which offers an easy way to initialize a {@link Channel} once it was
* registered to its {@link EventLoop}.
*
* Implementations are most often used in the context of {@link Bootstrap#handler(ChannelHandler)} ,
* {@link ServerBootstrap#handler(ChannelHandler)} and {@link ServerBootstrap#childHandler(ChannelHandler)} to
* setup the {@link ChannelPipeline} of a {@link Channel}.
*
* Be aware that this class is marked as {@link Sharable} and so the implementation must be safe to be re-used.
*
* @param <C> A sub-type of {@link Channel}
*/
@Sharable
public abstract class ChannelInitializer<C extends Channel> extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
ChannelHandlerContext是负责将ChannelHandler与ChannelPipeline相关联起来的桥梁- 如果同一个
ChannelHandler添加多次到ChannelPipeline中,那就会有多个ChannelHandlerContext对象与之对应
- 如果同一个
/**
* Enables a {@link ChannelHandler} to interact with its {@link ChannelPipeline}
* and other handlers. Among other things a handler can notify the next {@link ChannelHandler} in the
* {@link ChannelPipeline} as well as modify the {@link ChannelPipeline} it belongs to dynamically.
*
* <h3>Notify</h3>
*
* You can notify the closest handler in the same {@link ChannelPipeline} by calling one of the various methods
* provided here.
*
* Please refer to {@link ChannelPipeline} to understand how an event flows.
*
* <h3>Modifying a pipeline</h3>
*
* You can get the {@link ChannelPipeline} your handler belongs to by calling
* {@link #pipeline()}. A non-trivial application could insert, remove, or
* replace handlers in the pipeline dynamically at runtime.
*
* <h3>Retrieving for later use</h3>
*
* You can keep the {@link ChannelHandlerContext} for later use, such as
* triggering an event outside the handler methods, even from a different thread.
*
<pre>
* public class MyHandler extends {@link ChannelDuplexHandler} {
*
* <b>private {@link ChannelHandlerContext} ctx;</b>
*
* public void beforeAdd({@link ChannelHandlerContext} ctx) {
* <b>this.ctx = ctx;</b>
* }
*
* public void login(String username, password) {
* ctx.write(new LoginMessage(username, password));
* }
* ...
* }
* </pre>
*
* <h3>Storing stateful information</h3>
*
* {@link #attr(AttributeKey)} allow you to
* store and access stateful information that is related with a {@link ChannelHandler} / {@link Channel} and its
* context. Please refer to {@link ChannelHandler} to learn various recommended
* ways to manage stateful information.
*
* <h3>A handler can have more than one {@link ChannelHandlerContext}</h3>
*
* Please note that a {@link ChannelHandler} instance can be added to more than
* one {@link ChannelPipeline}. It means a single {@link ChannelHandler}
* instance can have more than one {@link ChannelHandlerContext} and therefore
* the single instance can be invoked with different
* {@link ChannelHandlerContext}s if it is added to one or more {@link ChannelPipeline}s more than once.
* Also note that a {@link ChannelHandler} that is supposed to be added to multiple {@link ChannelPipeline}s should
* be marked as {@link io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler.Sharable}.
*
* <h3>Additional resources worth reading</h3>
* <p>
* Please refer to the {@link ChannelHandler}, and
* {@link ChannelPipeline} to find out more about inbound and outbound operations,
* what fundamental differences they have, how they flow in a pipeline, and how to handle
* the operation in your application.
*/
public interface ChannelHandlerContext extends AttributeMap, ChannelInboundInvoker, ChannelOutboundInvoker
5.1.2.3 配置处理器配置的适配器 调用ServerBootstrapAcceptor构造方法
ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
final Channel channel, EventLoopGroup childGroup, ChannelHandler childHandler,
Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] childOptions, Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] childAttrs) {
this.childGroup = childGroup;
this.childHandler = childHandler;
this.childOptions = childOptions;
this.childAttrs = childAttrs;
// Task which is scheduled to re-enable auto-read.
// It's important to create this Runnable before we try to submit it as otherwise the URLClassLoader may
// not be able to load the class because of the file limit it already reached.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1328
enableAutoReadTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
channel.config().setAutoRead(true);
}
};
}
5.1.2.4 addLast方法
回到5.1.2.2
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();得到的是DefaultChannelPipeline
所以进入DefaultChannelPipeline的addLast方法。
public final ChannelPipeline addLast(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
synchronized (this) {
checkMultiplicity(handler);
newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler);
addLast0(newCtx);
// If the registered is false it means that the channel was not registered on an eventLoop yet.
// In this case we add the context to the pipeline and add a task that will call
// ChannelHandler.handlerAdded(...) once the channel is registered.
if (!registered) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
callHandlerAddedInEventLoop(newCtx, executor);
return this;
}
}
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
5.1.2.4.1 创建ChannelHandlerContext,并将ChannelHandler放入其中
进入newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler)
newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler);
DefaultChannelHandlerContext(
DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
super(pipeline, executor, name, handler.getClass());
this.handler = handler;
}
5.1.2.4.2 将创建好ChannelHandlerContext放入ChannelPipeline中,并添加到尾结点的前一个节点
private void addLast0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = tail.prev;
newCtx.prev = prev;
newCtx.next = tail;
prev.next = newCtx;
tail.prev = newCtx;
}
5.1.2.4.3 如果channel没有注册到eventLoop的话会将创建出的ChannelHandlerContext放入
if (!registered) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
private void callHandlerCallbackLater(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, boolean added) {
assert !registered;
PendingHandlerCallback task = added ? new PendingHandlerAddedTask(ctx) : new PendingHandlerRemovedTask(ctx);
PendingHandlerCallback pending = pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
if (pending == null) {
pendingHandlerCallbackHead = task;
} else {
// Find the tail of the linked-list.
while (pending.next != null) {
pending = pending.next;
}
pending.next = task;
}
}
到目前为止,准确的说**ChannelPipeline**里面存放的是一个个**ChannelHandlerContext**,而**ChannelHandlerContext**里面含有**ChannelHandler**
5.1.2.4.4 获取ChannelHandlerContext里面的ChannelHandler,并将ChannelHandlerContext放入其中。(要等channel注册到eventLoop。registered为true才会执行)
到这里, ChannelHandlerContext和 ChannelHandler相当于相互引用。
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
final void callHandlerAdded() throws Exception {
// We must call setAddComplete before calling handlerAdded. Otherwise if the handlerAdded method generates
// any pipeline events ctx.handler() will miss them because the state will not allow it.
if (setAddComplete()) {
handler().handlerAdded(this);
}
}